Understanding Autism and Depression
Autism and depression are two distinct yet interconnected conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s life. Understanding the nature of autism, the complexities of depression, and the relationship between the two is essential for recognizing and addressing symptoms effectively.

What is Autism?
Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a developmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. Individuals with autism may have difficulty understanding and expressing emotions, interpreting social cues, and engaging in reciprocal conversation.
Autism is a spectrum disorder, meaning it varies in severity and can manifest differently in each person.
What is Depression?
Depression is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, and a lack of energy or motivation. It affects a person’s emotional well-being and overall functioning. Depression can occur in individuals with or without autism, but its presence in individuals on the autism spectrum may present unique challenges.
The Connection Between Autism and Depression
Research has identified a significant connection between autism and depression. Individuals with autism are at a higher risk of experiencing depressive symptoms compared to the general population. The reasons for this connection are multifaceted and can be influenced by various factors such as social challenges, sensory sensitivities, and difficulty with emotional regulation.
It is important to note that not all individuals with autism will experience depression, and the severity of depressive symptoms can vary widely. However, recognizing and addressing the potential co-occurrence of autism and depression is crucial for providing appropriate support and treatment.
Understanding the distinct characteristics of autism and depression is the first step in identifying and addressing symptoms effectively. By acknowledging the complexities of these conditions and their connection, individuals with autism and their support networks can work together to promote mental well-being and improve quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Autism
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder that can manifest in various ways. While each individual with autism is unique, there are common symptoms that are often observed. Understanding these symptoms can help individuals with autism and their loved ones navigate the challenges they may face. Here are some of the common symptoms associated with autism:
Social Challenges and Isolation
People with autism often experience difficulties in social interactions and forming meaningful connections with others. They may struggle with understanding social cues, such as body language and facial expressions, making it challenging to engage in conversations and build relationships. Consequently, individuals with autism may feel isolated and find it hard to connect with their peers.

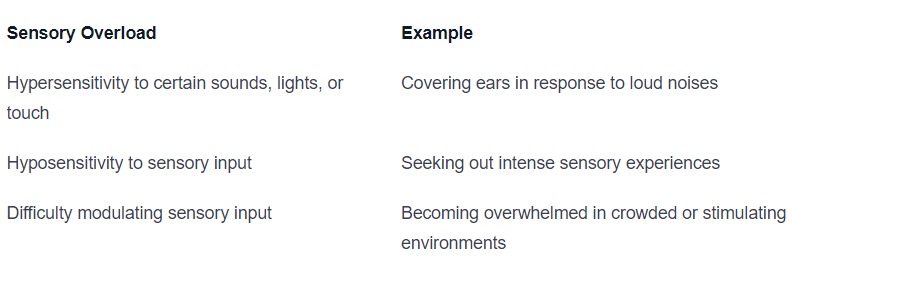
Sensory Overload and Meltdowns
Sensory Processing Issues are commonly associated with autism. Individuals with autism may experience sensory overload, where their brains have difficulty filtering and processing sensory information. This can result in hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to stimuli such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells. When overwhelmed, individuals with autism may have meltdowns or exhibit behaviors aimed at seeking sensory regulation.
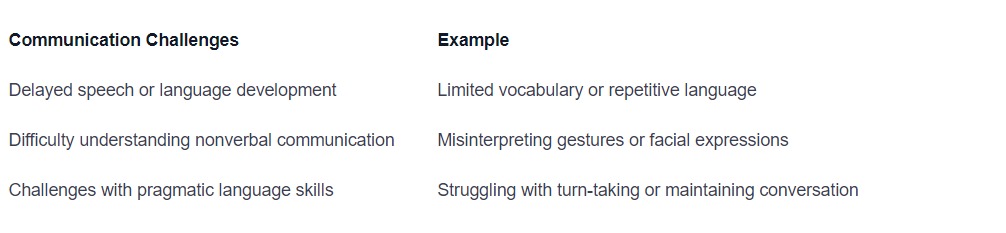
Difficulty with Communication and Expression
Expressive and Receptive Communication challenges are common among individuals with autism. They may have difficulty understanding and using verbal and nonverbal communication effectively. This can lead to difficulties expressing their needs, emotions, and thoughts, as well as understanding others. Some individuals with autism may rely on alternative forms of communication, such as visual supports or augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices.
Understanding these common symptoms of autism can provide insight into the challenges individuals with autism may face. It is important to remember that each person with autism is unique, and the severity and presentation of symptoms can vary. By recognizing and acknowledging these symptoms, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with autism.
Identifying Symptoms of Depression in Autism
Depression can often coexist with autism, presenting unique challenges for individuals on the autism spectrum. Identifying symptoms of depression in autism is crucial for timely intervention and support. Here are some common symptoms to be aware of:
Persistent Sadness and Lack of Interest
One of the primary symptoms of depression is a persistent feeling of sadness or low mood.
In individuals with autism, it can be challenging to recognize and express these emotions, making it crucial for caregivers and professionals to be vigilant. Look for signs of prolonged sadness, increased withdrawal from activities or interests, and a loss of motivation or enthusiasm.
Changes in Sleep Patterns and Appetite
Depression can impact sleep patterns and appetite, and this holds true for individuals with autism as well. Keep an eye out for significant changes in sleep, such as insomnia or excessive sleepiness. Similarly, pay attention to any noticeable changes in appetite, such as a significant decrease or increase in food consumption.

Low Energy and Fatigue
Individuals with autism who are experiencing depression may exhibit signs of low energy and fatigue. They may appear physically and mentally tired, lacking the usual level of energy and motivation. This can manifest as increased lethargy, reduced participation in activities, and a decline in overall functioning.
It is important to note that the symptoms of depression in autism can vary from person to person. Some individuals may exhibit more obvious signs, while others may display subtler indicators.
Regular communication and observation, along with input from healthcare professionals, can assist in identifying and addressing these symptoms effectively.
Overlapping Symptoms and Challenges
Individuals with both autism and depression often experience overlapping symptoms and face unique challenges that can further complicate their daily lives. Understanding these commonalities is crucial for providing effective support and intervention. Let’s explore some of the shared symptoms and challenges that individuals with autism and depression may encounter.
Difficulty Recognizing and Expressing Emotions
Both autism and depression can make it challenging for individuals to recognize and express their emotions effectively. People with autism may have difficulty understanding and interpreting the emotions of others, as well as expressing their own feelings in a way that others can understand. Similarly, individuals with depression may experience a persistent lack of interest or pleasure in activities they once enjoyed, which can further hinder their ability to express emotions.
Recognizing and addressing these difficulties is essential for promoting emotional well-being and communication. Providing individuals with the necessary tools and strategies to identify and express their emotions can greatly enhance their overall quality of life.
Executive Functioning and Daily Functioning
Executive functioning refers to a set of cognitive skills that are responsible for planning, organizing, and executing tasks. Both individuals with autism and depression may struggle with executive functioning, which can affect their ability to manage daily activities effectively.
Individuals with autism often face challenges in areas such as time management, prioritization, and organization, while those with depression may experience difficulties with motivation, concentration, and decision-making. These executive functioning difficulties can impact various aspects of their lives, including school, work, and personal relationships.
Supportive strategies, such as creating structured routines, providing visual aids, and breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps, can help individuals with autism and depression improve their executive functioning skills and enhance their daily functioning.
Increased Risk Factors
The co-occurrence of autism and depression can increase the risk factors associated with each condition. Research suggests that individuals with autism are more vulnerable to developing depression due to the social and communication challenges they often face. Similarly, individuals with depression may experience additional difficulties when also dealing with the unique characteristics of autism.
It is important to be aware of these increased risk factors and provide appropriate support and intervention. Early identification and intervention can help mitigate the impact of these challenges and improve overall well-being.
Understanding the overlapping symptoms and challenges between autism and depression is crucial for individuals, their families, and healthcare professionals. By recognizing these shared experiences, we can work towards providing tailored support and effective interventions to promote positive mental health outcomes for individuals with autism and depression.
Seeking Support and Treatment
When it comes to managing the challenges of autism and depression, seeking support and treatment is crucial. There are various options available to individuals with autism who are also experiencing symptoms of depression. In this section, we will explore therapy options, medication considerations, and the importance of building a supportive network.
Therapy Options for Autism and Depression
Therapy can play a significant role in helping individuals with autism and depression. Various therapeutic approaches can address the unique needs and challenges associated with both conditions. Some common therapy options include:

It’s important to work with a qualified therapist who has experience in both autism and depression to ensure that the therapy approach is tailored to individual needs.
Medication Considerations
In some cases, medication may be recommended to manage symptoms of depression in individuals with autism. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or other antidepressants may be prescribed to help alleviate depressive symptoms. However, medication should always be carefully considered, and the potential benefits and risks should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
It’s essential to work closely with a psychiatrist or medical professional who specializes in autism and mental health to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for each individual. Regular monitoring and communication are essential to assess the effectiveness of the medication and to address any potential side effects.
Building a Supportive Network
Building a supportive network is vital for individuals with autism and depression. Having a strong support system can provide emotional support, understanding, and encouragement throughout the journey. Here are some strategies for building a supportive network:
- Seek support from family and friends who are understanding and empathetic.
- Join support groups or online communities specifically for individuals with autism and depression.
- Connect with local or national autism organizations that offer support services and resources.
- Consider seeking guidance from a counselor or therapist who specializes in autism and depression.
- Engage in activities or hobbies that allow for social interaction and connection with like-minded individuals.
Remember, building a supportive network takes time, and it’s important to be patient with yourself. Surrounding yourself with individuals who understand and support your unique needs and challenges can make a significant difference in managing both autism and depression effectively.
The impact of depression on executive functioning and daily living skills
Depression can have a significant impact on executive functioning and daily living skills in individuals with autism. Executive functioning skills, such as planning, organizing, and decision-making, may be further impaired by the symptoms of depression. This can result in difficulties managing daily activities, such as maintaining personal hygiene or completing household tasks.
The impact of depression on daily living skills can also manifest in a lack of motivation and energy to engage in activities that were once enjoyed. Individuals with autism who are experiencing depression may withdraw from social interactions or preferred activities, leading to increased isolation and decreased quality of life.
It is important for caregivers and healthcare professionals to recognize the impact of depression on executive functioning and daily living skills in individuals with autism. Providing tailored support and interventions can help mitigate the effects of depression on these critical areas of functioning and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
Individuals with autism may face unique challenges, including difficulties with communication, sensory regulation, and executive functioning. When depression co-occurs with autism, these challenges can be further complicated, leading to increased risk factors and decreased quality of life. By recognizing the shared symptoms and challenges between autism and depression, we can work towards providing tailored support and effective interventions for individuals who experience both conditions.
Therapy options, medication considerations, and building a supportive network are crucial components in managing the challenges of autism and depression. Seeking timely intervention and support is essential for promoting positive mental health outcomes.
It is important to remember that each person with autism is unique, and the presentation of symptoms may vary. By acknowledging these differences and providing individualized support, we can create a more inclusive environment for individuals with autism who also experience depression. With proper care and attention, individuals with autism can lead fulfilling lives while managing their mental health needs effectively.
Sources
- https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/news/science-news/2016/depression-and-autism-spectrum-disorder.shtml
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/psychotherapies/index.shtml
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/child-and-adolescent-mental-health/antidepressant-medications-for-children-and-adolescents-information-for-parents-and-caregivers.shtml

 We've just released an article! Check out our blog!
We've just released an article! Check out our blog! 


