ABA Therapy Overview
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis therapy, has been a widely used approach to help individuals with autism and related developmental disorders since the 1960s. It is considered an evidence-based best practice treatment by the US Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association, supported by scientific tests of its usefulness, quality, and effectiveness.

History and Effectiveness
The history of ABA therapy dates back to the 1960s when Dr. Ivar Lovaas pioneered the use of behavior analysis techniques to help children with autism. Since then, ABA therapy has evolved and gained recognition as an effective intervention for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ABA therapy in improving outcomes for individuals with autism. More than 20 studies have shown that intensive and long-term therapy using ABA principles can lead to significant improvements in intellectual functioning, language development, daily living skills, and social functioning.
Role of ABA Therapists
ABA therapists play a crucial role in implementing ABA therapy and helping individuals with autism improve their social, communication, and behavioral skills [2]. These trained professionals work closely with individuals with autism to assess their needs, develop treatment plans, and provide ongoing support.
The responsibilities of ABA therapists include behavior assessment, treatment planning, and family support. ABA therapists conduct a thorough assessment to understand the individual’s strengths, challenges, and specific behaviors that need to be addressed. Based on the assessment, they develop individualized treatment plans that outline specific goals and strategies to address the individual’s needs. ABA therapists also work closely with families, providing guidance and support to help them implement behavior management techniques and strategies in the home environment [3].
By utilizing behavior intervention plans, skill-building programs, and play simulations, ABA therapists create a structured and supportive environment to promote positive behavioral changes and skill development. They implement evidence-based techniques to reinforce desired behaviors, reduce problem behaviors, and teach new skills.
In summary, ABA therapy is an evidence-based approach that has proven effectiveness in improving outcomes for individuals with autism. ABA therapists play a vital role in implementing ABA principles, conducting assessments, developing treatment plans, and providing ongoing support to individuals with autism and their families.
Becoming an ABA Therapist
Becoming an Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapist requires a combination of education, experience, and certification. ABA therapists play a crucial role in helping individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities achieve their full potential through behavior modification techniques. Here are the key steps to becoming an ABA therapist.
Educational Requirements
To embark on a career as an ABA therapist, a bachelor’s degree in psychology, education, or a related field is typically required. While various degrees can be applicable, a degree in psychology is particularly beneficial, as it provides a solid foundation in the principles of behaviorism, which form the basis of ABA therapy. The coursework in these programs covers topics such as behavioral analysis, developmental psychology, and research methods.
Experience and Certification
Gaining hands-on experience is a vital step in becoming an ABA therapist. After completing a bachelor’s degree, aspiring ABA therapists typically work as behavior technicians under the supervision of a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA). This experience allows individuals to apply the principles and techniques of ABA therapy in real-world settings and develop the necessary skills to work with clients effectively.
To become a certified ABA therapist, completion of a certification program approved by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) is required. The BACB offers two levels of certification: Registered Behavior Technician (RBT) and Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA). The RBT certification is an entry-level certification that requires individuals to complete specific training and pass an exam, while the BCBA certification is for individuals who have obtained a master’s degree and have met additional requirements set by the BACB.
Continuing Education
To maintain certification as an ABA therapist, it is necessary to stay up-to-date with the latest research and techniques in the field. This is achieved through continuing education units (CEUs) that must be completed every two years. CEUs provide opportunities for ABA therapists to deepen their knowledge, enhance their skills, and stay current with the evolving best practices in ABA therapy.
In addition to the educational and certification requirements, it’s important to note that most states require ABA therapists to become licensed to practice. Furthermore, many employers prefer or require ABA therapists to be certified, especially if they wish to open their own practice.
By completing the necessary educational requirements, gaining practical experience, and obtaining the appropriate certification, individuals can pursue a rewarding career as an ABA therapist and make a positive impact on the lives of individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities.
Job Outlook for ABA Therapists
As the field of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) continues to grow, the job outlook for ABA therapists is promising. ABA therapists play a crucial role in providing therapeutic interventions to individuals with behavioral challenges. Let’s explore the growth trends and salary expectations for ABA therapists.
Growth Trends and Opportunities
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), ABA therapists are predicted to experience a job growth rate of more than 20% by 2029, indicating a strong job outlook for the future. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for ABA services in various settings, including schools, clinics, and homes.
All levels of ABA therapists, from bachelor’s to master’s level, are expected to see significant job growth by 2029. Therapists at the master’s level, such as Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs), are predicted to have a 22% job growth rate. Bachelor’s-level therapists are expected to experience a 25% growth rate, while social and human services assistants, including Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs), are projected to have a 17% growth rate.
The demand for BCBAs has shown remarkable growth in recent years. Between 2010 and 2018, the demand for BCBAs increased by 1,942%, and from 2017 to 2018 alone, it increased by 127%. This trend indicates a significant demand for professionals in the field, highlighting the favorable job outlook for behavior analysts.
Salary Expectations
When it comes to salary, ABA therapists are compensated for their specialized skills and expertise. The median hourly wage for ABA therapists is reported as $26.93, according to the National Bureau of Labor Statistics [7]. The top 10% of earners in this field make approximately $44.76 per hour, while the bottom 10% earn around $15.56 per hour.
It’s important to note that salaries can vary depending on factors such as experience, education level, location, and work setting. Some states offer higher hourly wages for ABA therapists, including Alaska, Nevada, Kentucky, Rhode Island, Georgia, Colorado, Ohio, Oregon, New Jersey, and Washington [7].
As the demand for ABA therapists continues to rise, it is expected that salaries will remain competitive, providing opportunities for growth and advancement in the field.
Considering the positive growth trends and salary expectations, pursuing a career as an ABA therapist can offer a rewarding and financially viable path.
ABA Therapy Techniques
ABA therapy utilizes various techniques to help individuals with behavioral challenges develop new skills, reduce problem behaviors, and improve their overall quality of life. In this section, we will explore three key techniques commonly employed by ABA therapists: behavior intervention plans, skill-building programs, and play simulation.
Behavior Intervention Plans
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) play a crucial role in ABA therapy. ABA therapists collaborate with teachers, parents, intervention specialists, staff, and the individual themselves to develop a comprehensive plan to address and decrease problematic behaviors. The BIP outlines strategies to replace undesirable behaviors with more appropriate alternatives [3].
The BIP is tailored to the unique needs of each individual and may include techniques such as positive reinforcement, prompting, and shaping. By implementing the BIP consistently, ABA therapists aim to minimize challenging behaviors and promote the acquisition of new, socially acceptable behaviors.
Skill-Building Programs
ABA therapists also create skill-building programs as part of the therapy process. These programs focus on teaching individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities a range of skills, including behaviorism cusp or pivotal behaviors. Behaviorism cusp skills enable individuals to access new environments, while pivotal behaviors help unlock and influence more complex skills without explicit teaching.
Skill-building programs are individualized and target various areas such as communication, social interactions, self-care, and academic skills. ABA therapists use evidence-based teaching strategies, such as discrete trial training and naturalistic teaching methods, to systematically teach and reinforce targeted skills. These programs promote progress and independence in daily functioning.
Play Simulation
Play simulation is another technique employed by ABA therapists to facilitate positive experiences and enhance social skills. ABA therapists engage in appropriate play activities with individuals, encouraging exploration, expression, and the development of positive social behaviors. Play simulation can also help reduce disruptive behaviors and increase communication skills.
Through play, ABA therapists create opportunities for individuals to practice important social skills, such as turn-taking, sharing, and following social norms. This technique allows individuals to gain confidence, build relationships, and engage in meaningful interactions with others.
By utilizing behavior intervention plans, skill-building programs, and play simulation, ABA therapists provide effective and individualized interventions to individuals with behavioral challenges. These techniques aim to improve behavior, enhance social skills, and promote overall well-being. ABA therapists play a vital role in implementing these evidence-based techniques, helping individuals reach their full potential in various settings such as hospitals, schools, community centers, and government agencies.
ABA Therapist Responsibilities
ABA therapists play a crucial role in providing effective therapy for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disabilities. They utilize evidence-based techniques to assess behavior, create treatment plans, and offer support to families and caregivers. The key responsibilities of an ABA therapist include behavior assessment, treatment planning, and family support.
Behavior Assessment
One of the primary responsibilities of an ABA therapist is conducting behavior assessments. This involves observing and analyzing the individual’s behavior patterns, identifying the antecedents and consequences that influence their behavior, and gathering relevant data. Through systematic assessment techniques, ABA therapists gain insights into the underlying factors contributing to challenging behaviors, as well as the individual’s strengths and areas for skill development.
Treatment Planning
Based on the behavior assessment, ABA therapists develop individualized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of the individual. These treatment plans are designed to address challenging behaviors, teach new skills, and promote overall development. ABA therapists implement behavior intervention plans (BIPs) to target inappropriate behaviors, decrease their occurrence, and teach alternative, more adaptive behaviors. BIPs are implemented collaboratively with various stakeholders, including teachers, parents, intervention specialists, staff, and the individual themselves, ensuring consistency and effectiveness.
Family Support
In addition to working directly with individuals, ABA therapists provide crucial support and guidance to families and caregivers. They help families understand the principles and techniques of ABA therapy, equipping them with the knowledge and skills to manage and support their loved ones effectively. ABA therapists collaborate with families to develop strategies that can be implemented at home and in other natural environments to reinforce and generalize skills targeted in therapy. This support extends beyond the therapy sessions, empowering families to actively participate in the individual’s progress and promote consistency in their learning and behavior management.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, ABA therapists contribute to the comprehensive and holistic treatment of individuals with ASD and other developmental disabilities. Their expertise in behavior assessment, treatment planning, and family support enables them to make a positive impact on the lives of those they serve. To become an ABA therapist, individuals often pursue certifications such as Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) or Assistant Behavior Analyst (ABA) after obtaining the necessary education and experience.
Specializations and Career Paths
For those interested in pursuing a career as an ABA therapist, there are various specializations and career paths to explore within the field. These opportunities allow individuals to apply their skills in different settings and work with diverse populations. In this section, we will discuss different roles in ABA, median annual salaries, and the importance of licensing and certification.
Different Roles in ABA
ABA therapists can pursue various roles in the field, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements. Some common roles include:
- ABA Therapist: These therapists work directly with individuals, implementing behavior intervention plans and providing support to clients and their families.
- ABA Training Coordinator: In this role, therapists oversee the training and supervision of other ABA professionals, ensuring quality and adherence to best practices.
- Clinical Supervisor: Clinical supervisors provide guidance and supervision to ABA therapists, ensuring the delivery of effective and ethical services.
- University Professor: ABA therapists with extensive experience and advanced degrees can pursue teaching positions in universities, sharing their knowledge and expertise with aspiring professionals.
- Clinical Director: Clinical directors oversee the overall operations of ABA programs, managing staff, implementing policies, and ensuring program effectiveness.
Median Annual Salaries
Salaries for ABA therapists can vary depending on factors such as experience, education, location, and job role. According to PayScale and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salaries for different ABA roles are as follows:
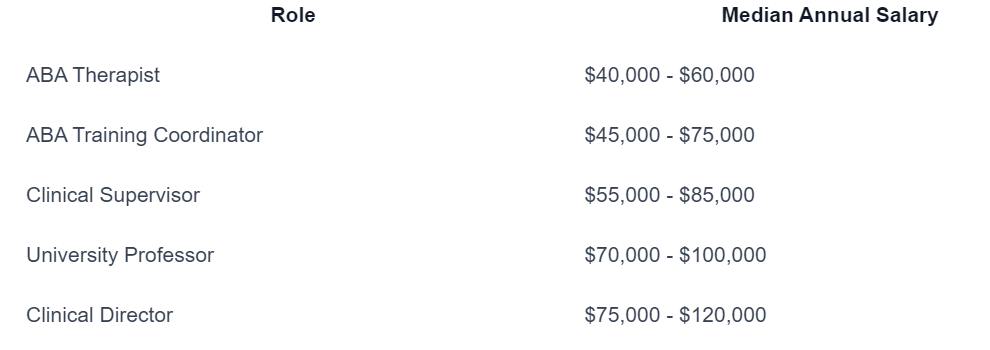
Figures courtesy of Regis College
It’s important to note that these figures are approximate and can vary based on factors such as location, experience, and employer. It’s advisable to research specific job markets and consult reliable sources for the most up-to-date salary information.
Licensing and Certification
Most states require ABA therapists to become licensed to practice, with specific prerequisites varying from state to state. Familiarizing oneself with the licensing and renewal requirements of the state in which they plan to practice is essential. Additionally, certification is typically required by employers and is crucial for ABA therapists who wish to open their own practice.
As of July 2021, more than 48,000 individuals had become board-certified behavior analysts, according to the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB). Certification demonstrates a high level of competence and adherence to ethical standards in the field.
By pursuing appropriate licensing and certification, ABA therapists can ensure they meet the necessary qualifications to practice and provide effective services to their clients.
When considering a career as an ABA therapist, it’s important to explore the various specializations and career paths available. Understanding the roles, salary expectations, and licensing/certification requirements will help individuals make informed decisions about their future in the field.
References
- https://www.autismspeaks.org/applied-behavior-analysis
- https://www.totalcareaba.com/autism/become-an-aba-therapist
- https://leafwingcenter.org/what-aba-therapists-do/
- https://online.regiscollege.edu/online-masters-degrees/master-science-applied-behavior-analysis/resources/how-to-become-an-applied-behavior-analyst-aba-therapist/
- https://elemy.wpengine.com/aba-therapists/job-growth
- https://www.crossrivertherapy.com/behavioral-analysts/job-growth
- https://www.jobhero.com/career-guides/careers/planning/how-to-become-aba-therapist

 We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!
We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!



