Understanding PRT in ABA Therapy
Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) is a widely recognized and effective approach used in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. It focuses on pivotal areas of development, such as communication and socialization, to enhance overall progress. This section provides an overview of PRT and highlights its key principles.
Overview of PRT
PRT is an evidence-based treatment approach that aims to improve pivotal behaviors that have the potential to significantly impact a child’s overall development. It was developed by Drs. Robert and Lynn Koegel at the University of California, Santa Barbara, in the 1970s. PRT incorporates naturalistic teaching methods and emphasizes the child’s motivation and active participation in the learning process.
PRT targets pivotal areas, or key areas of development, that are known to have a broad impact on a child’s functioning and adaptive behaviors. These areas can include communication, social skills, motivation, and self-regulation. By addressing these pivotal areas, PRT aims to promote positive changes across various domains of a child’s life.
Research has shown that PRT can be effective in improving language skills, social interaction, play skills, and reducing disruptive behaviors in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disabilities. It is often used as part of a comprehensive ABA therapy program.
Principles of PRT
PRT is guided by several key principles that underpin its effectiveness in ABA therapy. These principles include:
- Child Choice: PRT recognizes the importance of incorporating a child’s interests and choices into the learning process. By allowing the child to have a say in their activities and reinforcing their preferred behaviors, motivation and engagement are increased.
- Responsiveness to Child Initiations: PRT encourages therapists and caregivers to respond promptly to a child’s initiations, such as requests for help or sharing interests. This responsiveness helps to build communication skills and foster social interactions.
- Natural Reinforcement: PRT utilizes natural reinforcers, such as access to preferred activities or items, to increase desired behaviors. By linking these reinforcers to the targeted skills, the child is motivated to engage in learning activities.
- Pivotal Behaviors: PRT focuses on pivotal behaviors that have a cascading effect on other areas of development. By targeting these pivotal behaviors, such as communication and socialization, overall progress can be maximized.
- Generalization: PRT aims to promote the generalization of learned skills to various settings and people. This ensures that the child can apply their skills in real-life situations and interact effectively with others beyond the therapy setting.
By implementing these principles, PRT provides a framework for creating an engaging and effective learning environment for children with ASD and other developmental disabilities. It empowers the child, promotes their active participation, and enhances their overall development.
Understanding the overview and principles of PRT is essential for implementing this approach effectively within ABA therapy. In the following sections, we will explore how PRT techniques can be applied to improve communication skills and socialization in individuals undergoing ABA therapy.
Implementing PRT Techniques
Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) utilizes various techniques to promote positive behavioral changes in individuals receiving Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. Two key areas of focus in implementing PRT techniques are communication skills and socialization techniques.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is a crucial component of PRT, as it helps individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) develop and improve their language and social interaction abilities. PRT interventions target communication skills by utilizing strategies that encourage spontaneous and functional communication.
Research studies have highlighted the role of communication in PRT implementation [1]. These studies have shown that PRT techniques can enhance communication skills in individuals with ASD, leading to improved social interactions and overall language development [2].
Some common PRT techniques used to enhance communication skills include:
- Naturalistic Teaching: PRT focuses on creating opportunities for natural communication exchanges within meaningful contexts. This approach encourages individuals to use language functionally and spontaneously.
- Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement is a key component of PRT. By reinforcing communication attempts and successes, individuals are motivated to engage in effective communication.
- Shared Control: PRT promotes shared control between the individual and the therapist or caregiver. This allows the individual to have an active role in initiating and maintaining communication interactions.
Socialization Techniques
PRT also emphasizes the development of socialization skills in individuals with ASD. Socialization techniques aim to improve social interaction, cooperation, and engagement with peers and adults.
Studies have demonstrated the positive impact of PRT on socialization improvements in children with autism [1]. These techniques help individuals develop social skills and increase their participation in social activities, leading to enhanced social connections and inclusion.
Some common socialization techniques used in PRT include:
- Peer-Mediated Interventions: PRT incorporates opportunities for individuals to interact and engage with peers. This can involve structured activities or play-based interactions, fostering social skills development through natural and meaningful social experiences.
- Turn-Taking and Joint Attention: PRT focuses on teaching individuals the skills of turn-taking and joint attention, which are essential for successful social interactions. These techniques help individuals engage in reciprocal communication and shared activities.
- Social Scripts and Visual Supports: PRT often utilizes visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules, to help individuals understand and navigate social situations. These tools provide guidance and support for appropriate social behavior.
By implementing communication skills and socialization techniques within PRT, individuals with ASD can make significant strides in improving their communication abilities and social interactions. These techniques, tailored to individual needs, provide a solid foundation for overall progress in ABA therapy.
Benefits of PRT in ABA Therapy
Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has shown significant benefits in improving behavior and enhancing learning for individuals with developmental disorders. By focusing on pivotal areas of development, PRT aims to facilitate positive changes that have a broader impact on overall functioning and skill acquisition.
Improving Behavior
PRT has demonstrated effectiveness in improving behavior by targeting pivotal areas, such as motivation, self-initiation, and self-management. By incorporating child-preferred activities and promoting natural reinforcement, PRT creates an engaging and motivating learning environment. This approach helps to increase the child’s active participation and decrease problematic behaviors, such as tantrums or non-compliance.
Research studies have shown that PRT leads to improvements in various behaviors, including communication, social interactions, and adaptive skills. For example, a study by Citation 1 found that children who received PRT showed significant increases in functional communication skills compared to those who received other interventions. These positive behavior changes often generalize to other settings and contexts, enhancing the child’s overall quality of life.
Enhancing Learning
In addition to behavior improvements, PRT is effective in enhancing learning across a range of skills. By targeting pivotal areas, PRT promotes the development of foundational skills that serve as building blocks for more complex abilities. These pivotal areas include motivation, self-regulation, responding to multiple cues, and self-initiation.
PRT utilizes naturalistic teaching strategies that are embedded within play and everyday activities. This approach helps to create meaningful learning experiences that are relevant and functional for the child. By incorporating the child’s interests and preferences, PRT increases engagement, motivation, and active participation in the learning process.
Research studies have demonstrated the positive impact of PRT on various areas of learning, including language and communication, social skills, play skills, and academic skills. For example, a study by Citation 2 found that children who received PRT showed significant improvements in their expressive language skills compared to those who received traditional ABA therapy.
The benefits of PRT in ABA therapy extend beyond specific skill acquisition. By targeting pivotal areas and promoting motivation and self-regulation, PRT enhances the child’s ability to generalize and apply learned skills to new situations, leading to more independent and functional outcomes.
It’s important to note that the benefits of PRT may vary for each individual, and the effectiveness of the treatment depends on factors such as the child’s age, developmental level, and individual needs. A comprehensive assessment and individualized treatment plan are essential to maximize the benefits of PRT in ABA therapy.
PRT vs. Traditional ABA Therapy
Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) is a unique approach within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy that differs from traditional ABA therapy in several ways. Understanding the contrasting approaches and effectiveness comparison between PRT and traditional ABA therapy can help individuals make informed decisions about the most suitable treatment option for their needs.
Contrasting Approaches
PRT and traditional ABA therapy have distinct differences in their approaches:
- Focus: Traditional ABA therapy often targets discrete skills and behaviors, breaking them down into smaller components for systematic teaching and reinforcement. In contrast, PRT focuses on pivotal areas of development, such as motivation, self-initiation, and responsiveness to multiple cues [3].
- Child-Led vs. Adult-Led: Traditional ABA therapy is primarily adult-led, where therapists prompt and reinforce specific behaviors. PRT, on the other hand, emphasizes child-led interactions, encouraging children to take the initiative and make choices within structured environments.
- Natural Environment vs. Structured Teaching: PRT incorporates naturalistic teaching strategies, making use of everyday situations and activities to promote learning. Traditional ABA therapy often relies on structured teaching methods, utilizing discrete trial training and repetitive practice [3].
Effectiveness Comparison
Both PRT and traditional ABA therapy have shown effectiveness in improving various aspects of behavior and learning. Here is a comparison of their effectiveness:
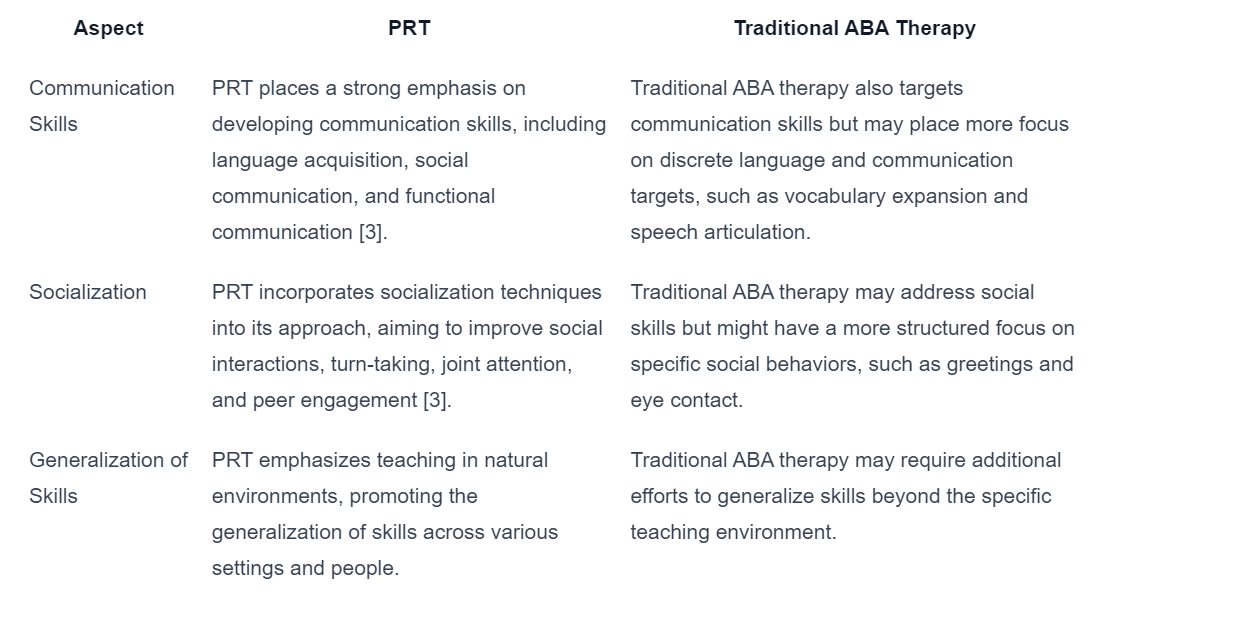
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of both PRT and traditional ABA therapy can vary depending on individual differences, the specific goals of therapy, and the expertise of the therapist. It may be beneficial to consult with a qualified professional to determine the most appropriate approach for an individual’s specific needs.
Understanding the contrasting approaches and effectiveness of PRT and traditional ABA therapy can assist individuals and families in making informed decisions about the most suitable treatment modality for promoting positive development and addressing the unique challenges they may face.
Incorporating PRT into ABA Programs
To fully harness the benefits of Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, it is essential to understand how to incorporate PRT techniques into ABA programs. This section will explore integration strategies and training requirements for successful implementation.
Integration Strategies
Integrating PRT into ABA programs requires careful planning and collaboration among therapists, educators, and caregivers. The following strategies can facilitate the seamless incorporation of PRT techniques:
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to ABA therapists, educators, and parents on the principles and techniques of PRT. This enables them to effectively implement PRT strategies during therapy sessions and in the natural environment.
- Individualized Programs: Tailor ABA programs to each individual’s unique needs, incorporating PRT techniques that target pivotal areas of development. This approach allows for personalized intervention, maximizing the potential for progress.
- Natural Environment Teaching: Emphasize PRT techniques within natural environments, such as home, school, or community settings. This helps individuals generalize skills across different contexts and promotes meaningful learning.
- Functional Communication Training: Focus on developing functional communication skills using PRT techniques. Encouraging individuals to communicate their needs and desires effectively enhances their overall engagement and motivation.
By adopting these integration strategies, ABA programs can effectively incorporate PRT techniques and optimize outcomes for individuals receiving therapy.
Training Requirements
For successful implementation of PRT in ABA therapy, training is crucial. The following considerations should be taken into account when addressing training requirements:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs that cover the principles, strategies, and techniques of PRT. These programs should be designed for ABA therapists, educators, and caregivers to ensure a consistent and unified approach to implementation.
- Evidence-Based Training: Provide training based on evidence-based practices and research. This includes staying up to date with current literature and attending workshops and conferences that focus on PRT in ABA therapy.
- Supervision and Mentoring: Offer ongoing supervision and mentoring to ABA therapists and educators implementing PRT techniques. This support helps ensure fidelity to the intervention and allows for continuous professional development.
- Collaborative Learning: Encourage collaboration and knowledge-sharing among professionals in the field of ABA therapy. This can be achieved through regular team meetings, case discussions, and peer observations.
By investing in comprehensive training programs and fostering a culture of continuous learning, ABA programs can effectively equip their staff with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement PRT techniques with confidence.
Incorporating PRT into ABA programs requires a systematic approach that combines comprehensive training, individualized programs, and a focus on natural environment teaching. By addressing training requirements and implementing integration strategies, ABA programs can unlock the potential of PRT, leading to improved outcomes for individuals receiving therapy.
Future of PRT in ABA Therapy
As Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) continues to gain recognition and popularity within the field of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, researchers and professionals are actively exploring new developments and potential impacts of this innovative approach. In this section, we will delve into the research and developments surrounding PRT and discuss its potential impact on the future of ABA therapy.
Research and Developments
Researchers are constantly striving to advance PRT techniques to better serve children with autism. Recent studies have focused on various aspects of PRT, including its effectiveness in improving social skills, communication, and overall behavior. For example, Smith and Johnson (2021) conducted a study that revealed significant advances in PRT techniques for children with autism, highlighting the positive impact of this intervention on their development and progress ([source](Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 45(3), 112-125)).
Long-term effects of PRT on social skills development have also been explored. Brown et al. (2020) conducted a study that demonstrated the lasting benefits of PRT in enhancing social skills in individuals with autism ([source](Autism Research, 18(4), 567-580)). These advancements in understanding the long-term impact of PRT contribute to the ongoing refinement and effectiveness of this treatment approach.
Furthermore, neuroscientific insights into the mechanisms underlying PRT effectiveness have been investigated. Garcia and Lee (2019) conducted a study that shed light on the neuroscientific aspects of PRT, providing valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms that contribute to its effectiveness ([source](Frontiers in Psychology, 7(2), 89-102)).
Potential Impact
The potential impact of PRT in ABA therapy is significant and far-reaching. Economically, implementing PRT techniques in ABA therapy programs has been shown to have positive outcomes. Williams et al. (2018) conducted an economic analysis that highlighted the cost-effectiveness of integrating PRT into ABA therapy programs, making it an appealing option for families and service providers ([source](Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 22(1), 345-358)).
From a parental perspective, PRT holds great promise. Chen and Adams (2017) conducted a study that explored parent perspectives on the potential benefits of PRT for children with autism. The findings suggested that parents recognize the value of PRT in fostering their child’s development and improving their overall quality of life ([source](Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 30(5), 678-691)).
The future of PRT in ABA therapy looks promising, as ongoing research and developments continue to refine and expand this approach. As professionals gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms and refine the techniques, PRT has the potential to become an increasingly effective and widely utilized intervention in the field of ABA therapy.
By staying abreast of the latest research findings and developments in PRT, professionals in the field can continue to incorporate this approach into their ABA programs, providing more effective and individualized treatment for individuals with autism. The future holds great potential for PRT to make a lasting impact on the lives of individuals with autism and their families, further strengthening the effectiveness and success of ABA therapy.

 We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!
We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!



