Understanding Positive Reinforcement
In the realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, positive reinforcement plays a crucial role in shaping behavior and promoting positive outcomes. Let’s explore the foundations of ABA therapy and the role of reinforcers in this therapeutic approach.
Foundations of ABA Therapy
Positive reinforcement is one of the foundational building blocks of ABA therapy. It is a technique that involves adding a stimulus after a behavior, resulting in an increased likelihood for that behavior to occur in the future. By focusing on reinforcing desired behaviors, ABA therapy aims to enhance functional skills and improve overall quality of life for individuals.
Role of Reinforcers
Reinforcers play a vital role in ABA therapy. They are individualized stimuli that, when provided after a behavior, can increase the frequency, magnitude, or duration of that behavior. Identifying what serves as a reinforcer for each individual is crucial in tailoring the therapy to their specific needs and preferences.
Reinforcers can take various forms, including verbal praise, tangible items, physical contact, enjoyable activities, or other rewards. The effectiveness of a reinforcer depends on its value to the individual receiving it. For example, a child may find praise from a caregiver to be highly reinforcing, while another child may be motivated by earning tokens towards a preferred activity or item.
The role of reinforcers in ABA therapy is to strengthen desired behaviors and increase the likelihood of their recurrence. By consistently pairing these reinforcers with specific behaviors, individuals can learn and acquire new skills while reducing challenging behaviors.
Understanding the foundations of ABA therapy and the role of reinforcers is essential to implement positive reinforcement effectively. In the following sections, we will explore different positive reinforcement techniques and their practical applications in ABA therapy.
Implementing Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a fundamental aspect of ABA therapy, focusing on increasing desirable behaviors and decreasing undesirable behaviors through the use of rewards and incentives. In this section, we will explore some key elements of implementing positive reinforcement in ABA therapy, including token economies, immediate vs. delayed reinforcement, and continuous vs. intermittent reinforcement.
Token Economies in ABA
One commonly used method in ABA therapy is the implementation of token economies. Token economies involve identifying target behaviors, choosing tokens as a form of immediate reinforcement, using a rewards chart, and providing backup reinforcers. This method allows children to visualize their progress, self-monitor their behaviors, and learn to accept delayed gratification.
The rewards chart serves as a visual representation of the desired behaviors and the tokens earned. Tokens can be in the form of stickers, points, or other tangible objects. These tokens can then be exchanged for backup reinforcers such as preferred items, activities, or privileges. Token economies help reinforce positive behaviors consistently and provide a structured approach to positive reinforcement within ABA therapy.
Immediate vs. Delayed Reinforcement
In ABA therapy, the timing of reinforcement plays a crucial role in its effectiveness. Immediate reinforcement involves providing a reward or consequence immediately following the desired behavior. This helps individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) associate the behavior with the positive outcome, making it more likely for them to engage in that behavior again.
Delayed reinforcement, on the other hand, involves providing the reward or consequence after a certain time delay. This technique can be useful for teaching individuals to accept delayed gratification and helps with long-term behavior change [2]. It is important to carefully consider the individual’s ability to tolerate delays and gradually increase the delay as they become more proficient in their skills.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Reinforcement
When initially teaching a new behavior or skill, it is often recommended to use continuous reinforcement. Continuous reinforcement involves reinforcing all occurrences of the target behavior. This method helps establish a strong connection between the behavior and its consequences, allowing individuals to learn and understand the desired behavior more quickly.
Once a behavior has been well established, transitioning to intermittent reinforcement is recommended. Intermittent reinforcement involves reinforcing the behavior only occasionally. This technique helps maintain the behavior after it has been learned and reduces the dependency on constant reinforcement. It is important to find the balance between reinforcement frequency and maintaining the behavior over time [2].
By implementing token economies, considering the timing of reinforcement, and utilizing continuous and intermittent reinforcement techniques, positive reinforcement becomes a powerful tool in ABA therapy. These strategies help individuals with ASD associate positive outcomes with desired behaviors, promote skill acquisition, and reduce problem behaviors. It is important to personalize treatment plans and choose reinforcement strategies that best suit each individual’s needs and goals within the ABA therapy process.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
In Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, positive reinforcement is a fundamental technique aimed at increasing desirable behaviors and decreasing undesirable behaviors. It involves providing a reward or consequence immediately following a desired behavior, with the goal of increasing the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. Positive reinforcement helps individuals associate the desired behavior with a positive outcome, making it more likely for them to engage in that behavior.
Verbal Praise and Rewards
Verbal praise is a commonly used positive reinforcement technique in ABA therapy. It involves providing specific and genuine verbal recognition for a desired behavior. The use of positive, encouraging words and expressions acknowledges and reinforces the individual’s efforts and achievements. Verbal praise can be tailored to the individual’s preferences, such as providing specific compliments or using a preferred tone of voice. It is a powerful tool that helps build self-esteem and motivates individuals to continue engaging in the desired behavior.
Rewards, such as tokens or points, can also be employed as a form of positive reinforcement. These tokens can be accumulated and exchanged for preferred items, activities, or privileges. Token economies, in which individuals earn tokens for demonstrating desired behaviors, are often used in ABA therapy. This technique allows for the reinforcement of positive behaviors consistently and provides a visual representation of progress and rewards.
Tangible Items and Activities
Tangible items and activities can be effective positive reinforcers, especially when they align with the individual’s interests and preferences. These can include toys, stickers, small treats, or other items that hold value to the individual. By offering tangible rewards, individuals are motivated to engage in the desired behavior, as they associate it with receiving something they enjoy. It is important to consider the individual’s specific interests and preferences to ensure the effectiveness of the reinforcement.
Engaging in preferred activities can also serve as a positive reinforcement technique. By incorporating activities the individual enjoys, such as playing a game, listening to music, or participating in a hobby, therapists can reinforce desired behaviors and create a positive association with those behaviors. This helps to promote motivation and engagement in the therapy process.
Individualized Reinforcers
Individualized reinforcers are tailored to the unique preferences and needs of each individual. These reinforcers can range from specific activities or items to social interactions or natural consequences. The choice of reinforcement depends on the individual’s preferences, needs, and the specific behavior being targeted.
By personalizing the reinforcement strategy, therapists can maximize its effectiveness. For example, if an individual finds social interactions rewarding, using verbal praise and social interactions as positive reinforcement can be highly motivating. Alternatively, if an individual is motivated by a specific item or activity, incorporating that into the reinforcement plan can further enhance the desired behaviors.
Individualized reinforcers help create a positive and supportive therapeutic environment, fostering intrinsic motivation, skill development, and overall engagement in the therapy process.
Positive reinforcement techniques, including verbal praise, tangible items and activities, and individualized reinforcers, play a vital role in ABA therapy. These techniques enhance positive behaviors, build self-esteem, foster a positive self-image, and motivate individuals to learn and develop new skills. By utilizing positive reinforcement, therapists can shape behavior, promote skill development, and facilitate long-term behavior change in a safe and humane manner [5].
Positive Reinforcement in Practice
Positive reinforcement plays a pivotal role in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, a widely recognized approach for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This technique involves providing rewards or incentives immediately following a target behavior, increasing the likelihood of that behavior being repeated in the future. Let’s explore the effectiveness of positive reinforcement in ABA therapy and its impact on individuals with ASD.
Effectiveness in ABA Therapy
Positive reinforcement has been proven effective in improving a variety of behaviors and skills in individuals with ASD. It is a powerful tool used to encourage and strengthen desired behaviors, ultimately helping individuals reach their full potential and lead happier, more fulfilling lives. By reinforcing positive behaviors, ABA therapists can effectively teach new skills, promote compliance, and reduce problem behaviors.
ABA therapy utilizes positive reinforcement to create positive associations with desired behaviors. By consistently pairing these behaviors with rewards or incentives, individuals with ASD are motivated to engage in the desired behaviors more frequently. This leads to skill acquisition, improved social interactions, and enhanced independence [5].
Impact on Individuals with ASD
Positive reinforcement in ABA therapy has a profound impact on individuals with ASD. It fosters a supportive and encouraging environment that focuses on strengths and achievements. Through the use of rewards, such as verbal praise, tangible items, physical contact, or enjoyable activities, individuals with ASD are motivated to engage in positive behaviors and develop important life skills.
By utilizing positive reinforcement, ABA therapists can effectively address challenging behaviors and replace them with more appropriate and functional behaviors. This not only improves the individual’s quality of life but also enhances their ability to communicate, learn, and engage in social interactions. The positive experiences and rewards associated with desired behaviors create a foundation for long-term success and personal growth.
In conclusion, positive reinforcement is a fundamental technique in ABA therapy, proving to be highly effective in improving behaviors and skills in individuals with ASD. By utilizing this approach, therapists can create positive associations with desired behaviors, promote skill acquisition, and enhance the overall well-being of individuals with ASD.
Comparison with Punishment
When it comes to behavior modification in ABA therapy, positive reinforcement plays a central role. It is often preferred over punishment techniques due to its potential negative side effects. Positive reinforcement focuses on adding something to the environment to encourage desired behaviors, while positive punishment involves taking something away to decrease undesirable behaviors.
Positive vs. Negative Techniques
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone technique in ABA therapy, aimed at increasing desirable behaviors and decreasing undesirable behaviors. It is achieved through various methods, such as verbal praise, tangible items, physical contact, enjoyable activities, or other rewards. By adding these positive elements to the individual’s environment, they are more likely to engage in the desired behaviors, as they associate them with pleasant experiences.
On the other hand, positive punishment involves the application of an aversive stimulus or the removal of a positive stimulus to decrease undesirable behaviors. While punishment techniques may seem effective initially, they can have negative side effects, such as increased aggression, anxiety, or avoidance behaviors. This is particularly crucial when working with individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), who may be more sensitive to negative stimuli.
To further highlight the differences between positive reinforcement and positive punishment, consider the following table:
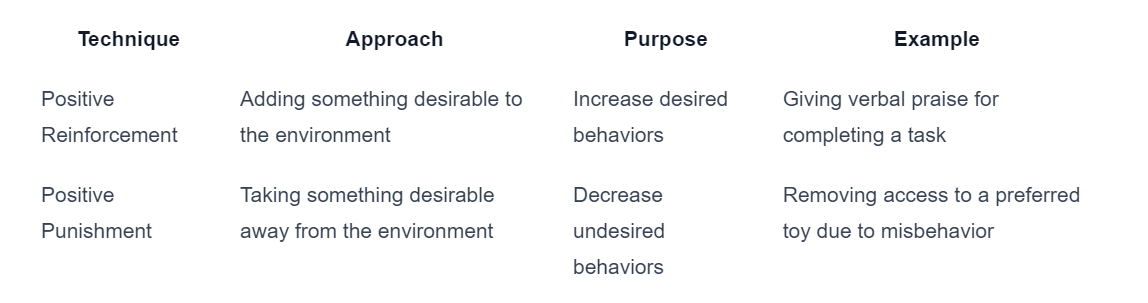
Table based on information from Discovery ABA and Empower Behavioral Health
By utilizing positive reinforcement techniques in ABA therapy, individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can be motivated to engage in positive behaviors and achieve positive outcomes. It is important to create a supportive and nurturing environment that focuses on reinforcing desired behaviors rather than relying on punishment methods that may have unintended consequences.
Considerations in ABA Therapy
When it comes to Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, there are important considerations to keep in mind to ensure its effectiveness and success. Two key aspects to consider are personalized treatment plans and reinforcement strategies.
Personalized Treatment Plans
In ABA therapy, personalized treatment plans are the cornerstone of successful interventions for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These plans are developed based on comprehensive assessments that take into account the specific needs, preferences, and motivators of each client. By tailoring the treatment plan to the individual, therapists can create an environment that encourages positive behaviors and facilitates the learning of new skills.
Personalized treatment plans in ABA therapy involve setting specific goals and objectives for each individual. These goals are designed to address the unique challenges and needs of the person with ASD. By breaking down complex skills into manageable steps, therapists can reinforce each step along the way, making it easier for individuals to learn and progress. This individualized approach ensures that therapy is targeted and effective for each individual.
Reinforcement Strategies
Reinforcement strategies play a crucial role in ABA therapy, with positive reinforcement being a key component. Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors by adding something to the environment, thereby increasing the likelihood of the behavior being repeated in the future under similar conditions. These rewards can take various forms, such as praise, tokens, tangible items, or preferred activities, depending on the individual’s interests and preferences.
In ABA therapy, reinforcement strategies are carefully selected based on the individual’s needs and motivators. By identifying what is meaningful and rewarding for the individual, therapists can effectively reinforce positive behaviors and create a supportive environment that encourages learning and skill development. The use of individualized reinforcement strategies ensures that therapy remains engaging and motivating for each client.
It’s important to note that reinforcement strategies may vary depending on the individual and the specific goals of therapy. Therapists, often Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs), conduct comprehensive assessments to identify the most effective reinforcement strategies for each individual. These strategies are then incorporated into the personalized treatment plans to achieve optimal outcomes.
By considering the individualized nature of treatment plans and the selection of appropriate reinforcement strategies, ABA therapy can be tailored to meet the unique needs of individuals with ASD. This personalized approach, combined with positive reinforcement, enhances the effectiveness of ABA therapy and promotes positive behaviors, skill acquisition, and overall success.
References
- https://www.abtaba.com/blog/positive-reinforcement-aba-therapy
- https://www.fortahealth.com/resources/ways-to-use-positive-reinforcement-in-aba-therapy
- https://www.discoveryaba.com/aba-therapy/positive-reinforcement
- https://www.goldstarrehab.com/parent-resources/positive-reinforcement-in-aba-therapy
- https://www.empowerbh.com/blog/how-does-applied-behavior-analysis-utilize-positive-reinforcement/

 We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!
We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!