Understanding Autism Meltdowns
When it comes to autism meltdowns, it is crucial to understand the key aspects that differentiate them from temper tantrums and to explore the causes and triggers behind these intense reactions.
Differentiating Meltdowns from Tantrums
Autism meltdowns are not the same as temper tantrums. It is important to recognize that meltdowns are not a deliberate attempt to manipulate a situation or misbehavior. Here are some key differences:
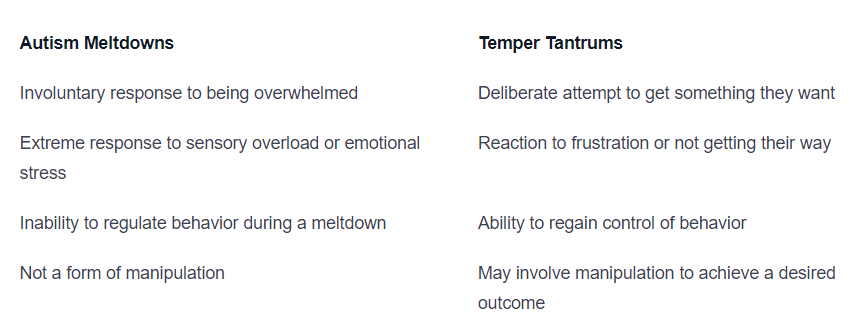
By understanding these distinctions, it becomes clear that meltdowns are a result of being unable to cope with stress or anxiety, rather than a deliberate act of defiance.
Causes and Triggers of Meltdowns
Autism meltdowns can be triggered by various factors, including sensory input, anxiety, or unexpected changes in routine. The overwhelming nature of these situations can lead to an intense response that is often more severe than a typical temper tantrum. It is important to note that meltdowns are not deliberate acts but are coping mechanisms to relieve intense stress or anxiety.
To better support individuals during meltdowns, it is crucial to identify the specific triggers and warning signs. By understanding the underlying causes and recognizing the early signs of distress, caregivers and support networks can intervene appropriately and provide the necessary assistance to help manage and prevent meltdowns.
By differentiating autism meltdowns from tantrums and understanding the causes and triggers behind these intense reactions, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Signs and Behaviors During Meltdowns
Autism meltdowns are intense responses to overwhelming situations, characterized by uncontrollable outbursts that may manifest physically, verbally, or both. It is important to differentiate meltdowns from tantrums, as they are often more severe and are a result of being unable to cope with stress or anxiety. Understanding the signs and behaviors that occur during meltdowns is crucial for providing appropriate support and creating a safe environment for individuals with autism.
Physical Manifestations of Meltdowns
During an autism meltdown, individuals may display a range of physical behaviors as a response to their overwhelming emotions. Some common physical manifestations of meltdowns include:
- Crying and Screaming: Intense emotional distress can lead to crying and screaming. This vocal expression of distress may be loud and prolonged.
- Hitting and Kicking: Some individuals may exhibit aggressive behaviors during meltdowns, such as hitting or kicking. These actions are not intentional acts of violence but rather a way of expressing frustration or releasing emotional tension.
- Biting or Spitting: In some cases, individuals with autism may resort to biting or spitting as a form of communication or self-expression during meltdowns.
- Running Away: Feeling overwhelmed, individuals may attempt to escape from the overwhelming situation by running away, potentially putting themselves at risk.
It is crucial for caregivers and those around individuals with autism to provide support and understanding during these episodes. Creating a safe environment, free from potential hazards, can help prevent harm during meltdowns.
Emotional Responses During Meltdowns
Alongside the physical manifestations, emotional responses play a significant role in autism meltdowns. The emotional experience during a meltdown can vary from person to person, but some common emotional responses include:
- Fear and Anxiety: Meltdowns often arise from feelings of fear and anxiety due to overwhelming situations or stimuli. These emotions can intensify during a meltdown, making it challenging for individuals to regulate their responses.
- Frustration and Anger: The inability to cope with stress or anxiety can lead to feelings of frustration and anger, which may be expressed through aggressive behaviors.
- Overwhelm and Sensory Sensitivities: Sensory overload, such as loud noises, bright lights, or crowded environments, can contribute to the overwhelming experience during a meltdown. Individuals with autism may become more sensitive to their surroundings, exacerbating their emotional response.
Understanding the emotional responses during meltdowns is crucial for providing appropriate support. Calm and patient communication, along with a safe and quiet environment, can help individuals with autism navigate their intense emotions and gradually regain control.
By being aware of the physical manifestations and emotional responses that occur during autism meltdowns, caregivers and those around individuals with autism can better understand and support them during these challenging episodes. Creating a safe and understanding environment is key to helping individuals with autism navigate their meltdowns and move towards a sense of calm and emotional regulation.
Supporting Individuals during Meltdowns
When an individual with autism experiences a meltdown, it is crucial to provide them with support and create a safe environment to help them regain control. Understanding the best strategies for supporting individuals during meltdowns can make a significant difference in their well-being. Two essential aspects of this support include creating a safe and calm environment, as well as employing strategies for de-escalation and coping.
Creating a Safe and Calm Environment
During an autism meltdown, the individual may display behaviors such as screaming, crying, hitting, kicking, or running away. It is essential to prioritize their safety and the safety of those around them. Here are some strategies for creating a safe and calm environment during a meltdown:
- Remove potential hazards: Clear the immediate surroundings of any objects that could cause harm or damage during the meltdown.
- Provide a quiet space: Offer a designated area where the individual can retreat and feel safe. This space should be free from sensory overload, such as loud noises or bright lights.
- Minimize stimulation: Reduce external stimuli that may contribute to sensory overload. Dim the lights, lower the volume, or eliminate any triggers that may exacerbate the meltdown.
- Maintain a predictable environment: Stick to familiar routines and avoid sudden changes that may add to the individual’s anxiety or stress.
By creating a safe and calm environment, caregivers can help individuals with autism feel secure and supported during meltdowns, facilitating a quicker recovery.
Strategies for De-escalation and Coping
De-escalation techniques can help individuals with autism regain control and manage their emotions during a meltdown. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Remain calm: Stay composed and speak in a soothing, reassuring tone. Displaying a calm demeanor can help the individual feel more secure.
- Offer reassurance: Use simple and concise language to provide comfort and let the individual know that you are there to support them.
- Use visual aids: Visual supports, such as social stories or visual schedules, can assist in calming the individual and helping them understand what is happening.
- Respect personal space: Allow the individual to have their personal space if they prefer it. Touching or crowding them may escalate the situation further.
- Provide sensory tools: Offer items that the individual finds comforting, such as a weighted blanket, fidget toys, or noise-canceling headphones. These tools can help regulate sensory input and promote a sense of calm.
By implementing these de-escalation strategies, caregivers can help individuals with autism navigate meltdowns more effectively, promoting their emotional well-being and reducing the duration and intensity of the meltdown.
Supporting individuals during meltdowns requires patience, understanding, and a proactive approach. By creating a safe and calm environment and employing appropriate de-escalation techniques, caregivers can provide the support needed to help individuals with autism regain control and navigate overwhelming situations with greater ease.
Prevention and Management of Meltdowns
To effectively address and manage autism meltdowns, it is important to focus on prevention and developing appropriate coping mechanisms and support plans. By identifying triggers and warning signs, individuals with autism and their caregivers can work together to create a supportive environment that minimizes the likelihood of meltdowns.
Identifying Triggers and Warning Signs
One of the key steps in preventing autism meltdowns is identifying triggers and recognizing warning signs. Triggers can vary from person to person, but common examples include sensory overload, changes in routine, transitions, and communication difficulties. By understanding these triggers, caregivers and individuals with autism can take proactive measures to avoid or minimize exposure to them.
Early recognition of warning signs is crucial in preventing meltdowns from escalating. These signs may include increased anxiety, stimming behaviors, withdrawal, or other visible indicators of distress. By being attuned to these signals, appropriate interventions can be implemented to help prevent or de-escalate a meltdown.
Developing Coping Mechanisms and Support Plans
Once triggers and warning signs have been identified, it is important to develop coping mechanisms and support plans. Establishing routines and predictability can provide a sense of stability and security for individuals with autism. This can involve creating a structured schedule, using visual aids, and providing clear communication about upcoming events or changes in routine.
Sensory support is another crucial aspect of managing meltdowns. Understanding an individual’s sensory sensitivities and providing appropriate accommodations, such as noise-canceling headphones or sensory toys, can help regulate sensory input and prevent overload.
Teaching coping strategies is also essential. This can involve providing individuals with autism with tools to self-regulate, such as deep breathing exercises, visual or verbal prompts, or a designated safe space where they can retreat when feeling overwhelmed. Caregivers and educators can work together to teach and reinforce these coping strategies, empowering individuals with autism to better manage their emotions and reactions.
Communication plays a vital role in preventing meltdowns. Open and clear communication between individuals with autism and their caregivers can help address concerns or frustrations before they escalate. Establishing alternative communication methods, such as picture exchange systems or augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, can assist individuals with autism in expressing their needs and emotions effectively.
By focusing on prevention and implementing strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs, individuals with autism can develop the skills and support necessary to manage and reduce the frequency of meltdowns. It is important for caregivers, educators, and society as a whole to increase awareness, understanding, and provide proper support and accommodation for individuals with autism in order to create an inclusive and supportive environment.
Educating Caregivers and Society
Raising awareness and understanding about autism meltdowns is essential for caregivers, educators, and society as a whole. By increasing knowledge about these meltdowns, individuals with autism can receive the proper support and accommodation they need to navigate overwhelming situations with understanding and compassion.
Increasing Awareness and Understanding
Educating caregivers and society about autism meltdowns is crucial to dispel misconceptions and promote empathy. It’s important to recognize that autism meltdowns are not temper tantrums or deliberate misbehavior, but rather intense responses to overwhelming situations. They are a coping mechanism when individuals with autism are unable to cope with stress or anxiety. By understanding the distinction between meltdowns and tantrums, caregivers and society can provide the necessary support and accommodation.
Increasing awareness includes educating people about the signs and behaviors exhibited during meltdowns. These may include physical manifestations such as crying, screaming, hitting, or biting, as well as emotional responses like heightened anxiety or withdrawal. Recognizing these signs can help caregivers and society respond appropriately and provide the necessary assistance.
Providing Proper Support and Accommodation
To better support individuals during meltdowns, caregivers and society can implement strategies that focus on creating a safe and calm environment. This involves understanding the triggers and warning signs that precede a meltdown, as well as developing coping mechanisms and support plans.
By identifying the factors that contribute to meltdowns, such as sensory overload or difficulty in communication, caregivers and society can proactively address these challenges and reduce the likelihood of meltdowns. This may include providing sensory accommodations or implementing visual supports to aid communication.
It is also crucial to offer support and reassurance during and after a meltdown. Patience, understanding, and calming techniques can help the individual regain control and minimize the impact of the meltdown on their well-being and those around them. By providing proper support and accommodation, caregivers and society can create an inclusive environment that promotes the overall well-being of individuals with autism.
In conclusion, educating caregivers and society about autism meltdowns is vital for fostering understanding and empathy. Increasing awareness about the nature of meltdowns and providing appropriate support and accommodation can help individuals with autism navigate overwhelming situations more effectively. By working together, we can create a more inclusive and supportive society for everyone.
References
- https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/working-with-advanced-formatting/creating-and-highlighting-code-blocks
- https://www.corticacare.com/care-notes/autistic-meltdowns
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-an-autistic-meltdown-260154
- https://www.ambitiousaboutautism.org.uk/information-about-autism/behaviour/meltdowns-and-shutdowns
- https://www.myautism.org/informational-kits/what-causes-a-meltdown-amp-how-to-prevent-them
- https://www.autism.org.uk/advice-and-guidance/topics/behaviour/meltdowns/all-audiences
- https://www.abtaba.com/blog/autism-meltdowns/

 We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!
We've just released an article!
Check out our blog!



